A shadowy web, a part of the internet which is not indexed by traditional search engines, has sparked public interest due to its association with anonymity and illicit activities. Inside this dark realm there is a intricate economy that prospers on the exchange of goods and services that are commonly illegal or difficult to access in the surface web. Under the radar marketplaces have arisen as the virtual storefronts of this economy, where users can buy and sell everything from illegal substances and counterfeit items to hacking tools and stolen data.
These marketplaces function on a foundation of confidentiality and secrecy, employing cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin to enable transactions that do not disclose buyers' or sellers' identities. As more people start to wonder about the dark web, understanding its marketplaces becomes essential to understand the broader implications of this concealed economy. The allure of anonymity and the promise of unconstrained trade continue to draw users, raising questions about the law, ethics, and the future of trade in a technological era.
The Structure on this Dark Web
The dark web is a subset within our deep web, that encompasses all parts of the vast internet that are not indexed by traditional search engines. It requires specialized software and configurations to access, most notably through its Tor network. Such network anonymizes users, rendering it difficult to trace their activities. Consequently, the dark web operates separately in contrast to the surface web, where most online interactions occur.
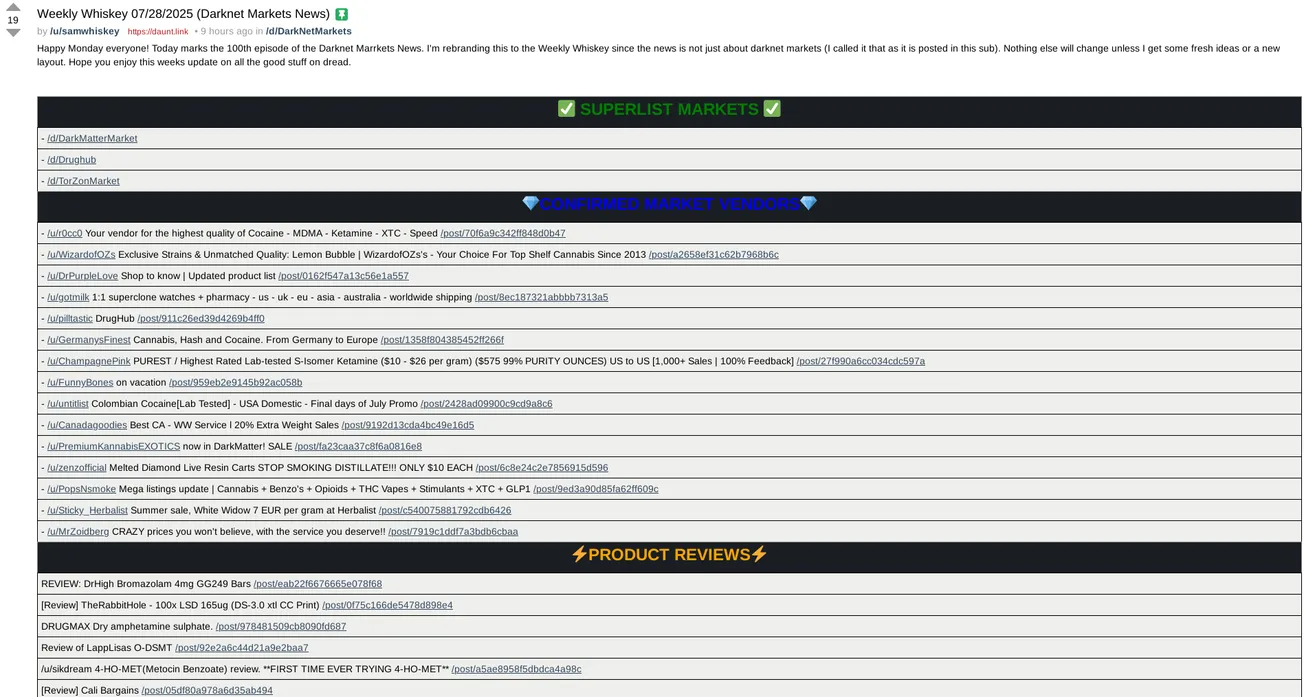
Inside the dark web, markets thrive in a variety niches, spanning from illicit goods to services. Such marketplaces are often organized similarly as popular e-commerce sites but run on the principle of anonymity and encryption. darknet markets 2026 create profiles, allowing them to showcase their offerings, and buyers rely on user reviews and feedback to navigate the often treacherous buying landscape. The competitive nature of these platforms drives innovation and adaptation for sellers.
The transactions that take place in dark web markets typically utilize cryptocurrencies, with Bitcoin being the most prominent. This financial anonymity provides another additional layer of security for both buyers and sellers. Despite the risks involved, the dark web economy has flourished, attracting those who seek to engage in activities not permissible in the mainstream marketplace. Understanding the structure remains crucial to comprehending the complexities and the dark web economy.

Exchanges in the Darkness
In the lawless world of the darkweb, exchanges happen away from the prying eyes of conventional oversight. Users take part in the buying and selling of illicit goods and services with a strong emphasis on anonymity. This environment fosters a sense of safety for clients and vendors alike, as they use cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin to conceal their identities and financial trails. The appeal of the deep web includes entry to items seldom found in regular marketplaces, from illicit drugs to counterfeit documents, all available at the press of a button.
Moreover, the framework of deep web marketplaces is designed to facilitate secure transactions. Escrow services are frequently employed, where payment is held until both parties fulfill their obligations. This system builds trust among users who might might be wary of scams or fraud. Feedback and ratings play a crucial role as well, allowing users to gauge the reliability of vendors. Such systems help maintain a semblance of organization within the chaos of illicit trading, encouraging repeat business.
However, the unstable nature of deep web markets poses substantial threats. Police agencies continuously observe these spaces, leading to frequent raids that can dismantle popular platforms instantly. This instability drives a constant cycle of new marketplaces emerging to take the spot of those that have been shut down. For participants, this means finding their way through a shifting landscape where security and legality are precarious at best, reminding everyone that while exchanges may be safe, the darkness of doubt are always looming.
Risks and Rules
Engaging with black market platforms involves significant dangers, both legal and individual. Users face the danger of facing law enforcement actions aimed at dismantling illegal activities. Many individuals have been detained as a result of actions targeting these platforms, highlighting the true risk of criminal charges, penalties, or imprisonment. Beyond legal consequences, there are risks related to frauds, as the disguise of transactions can lead to disputes over non-delivery of products or services.
The lack of oversight in the black market marketplace also raises concerns regarding security and safety. Online threats, such as cyber intrusions or ID fraud, are common on these marketplaces. Participants may unknowingly expose themselves to malware or scamming attacks when navigating these spaces, putting their personal information and financial data at risk. Additionally, the illegal nature of many products means that purchasers may be caught up in buying dangerous or harmful goods, increasing the likelihood for bad results.
Regulations surrounding the black market remain complex and often inefficient. While some areas have made progress in addressing the issues posed by these hidden markets, global collaboration is difficult due to varying laws and law enforcement abilities. As authorities continue to adjust to the changing landscape of the black market, participants must stay alert and informed about the legal implications of their actions, as well as the potential dangers inherent in participating with an uncontrolled market.
